Vertical Regridding#
Authors: Jason Boutte and Jill Zhang
Updated: 04/15/24 [xcdat v0.7.0]
Related APIs:
The data used in this example can be found through the Earth System Grid Federation (ESGF) search portal. We are using xarray’s OPeNDAP support to read a netCDF4 dataset file directly from its source. The data is not loaded over the network until we perform operations on it (e.g., temperature unit adjustment). More information on the xarray’s OPeNDAP support can be found here.
We’ll cover vertical regridding using xgcm. Two examples are outlined here to apply vertical regridding/remapping using ocean variables and atmosphere variables, respectively.
Notebook Setup#
Create an Anaconda environment for this notebook using the command below,
conda create -n xcdat_notebook -c conda-forge xcdat xesmf matplotlib ipython ipykernel cartopy nc-time-axis gsw-xarray jupyter
Activate the conda env with:
conda activate xcdat_notebook
Then create a kernel in your xcdat conda environment using ipykernel and name the kernel with the display name, e.g. xc070:
python -m ipykernel install --user --name xcdat_notebook --display-name xc070
Then to select the kernel xc070 in Jupyter to use the xcdat enviroment.
xesmfis required for horizontal regridding with xESMFmatplotlibis an optional dependency required for plotting with xarraync-time-axisis an optional dependency required formatplotlibto plotcftimecoordinatesgsw_xarrayis a wrapper for GSW-Python:the Python implementation of the Gibbs SeaWater (GSW) Oceanographic Toolbox of TEOS-10
Example 1: Remapping Ocean Variables#
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import xarray as xr
import xcdat
import numpy as np
# gsw-xarray is a wrapper for GSW-Python:
# the Python implementation of the Gibbs SeaWater (GSW) Oceanographic Toolbox of TEOS-10
import gsw_xarray as gsw
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
1. Open dataset#
[2]:
# urls for sea water potential temperature (thetao) and salinity (so) from the NCAR model in CMIP6
urls = [
"http://aims3.llnl.gov/thredds/dodsC/css03_data/CMIP6/CMIP/NCAR/CESM2/historical/r1i1p1f1/Omon/so/gn/v20190308/so_Omon_CESM2_historical_r1i1p1f1_gn_185001-201412.nc",
"http://aims3.llnl.gov/thredds/dodsC/css03_data/CMIP6/CMIP/NCAR/CESM2/historical/r1i1p1f1/Omon/thetao/gn/v20190308/thetao_Omon_CESM2_historical_r1i1p1f1_gn_185001-201412.nc",
]
ds = xr.merge([xcdat.open_dataset(x, chunks={"time": 4}) for x in urls])
# lev coordinate is in cm and bounds is in m, convert lev to m
with xr.set_options(keep_attrs=True):
ds.lev.load()
ds["lev"] = ds.lev / 100
ds.lev.attrs["units"] = "meters"
ds
2024-04-17 16:52:32,392 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:32,392 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:32,833 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:32,833 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
[2]:
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 117GB
Dimensions: (lev: 60, nlat: 384, nlon: 320, time: 1980, d2: 2, vertices: 4,
bnds: 2)
Coordinates:
* lev (lev) float64 480B 5.0 15.0 25.0 ... 5.125e+03 5.375e+03
* nlat (nlat) int32 2kB 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ... 378 379 380 381 382 383 384
* nlon (nlon) int32 1kB 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ... 314 315 316 317 318 319 320
lat (nlat, nlon) float64 983kB dask.array<chunksize=(384, 320), meta=np.ndarray>
lon (nlat, nlon) float64 983kB dask.array<chunksize=(384, 320), meta=np.ndarray>
* time (time) object 16kB 1850-01-15 13:00:00.000007 ... 2014-12-15 1...
Dimensions without coordinates: d2, vertices, bnds
Data variables:
time_bnds (time, d2) object 32kB dask.array<chunksize=(4, 2), meta=np.ndarray>
lat_bnds (nlat, nlon, vertices) float32 2MB dask.array<chunksize=(384, 320, 4), meta=np.ndarray>
lon_bnds (nlat, nlon, vertices) float32 2MB dask.array<chunksize=(384, 320, 4), meta=np.ndarray>
lev_bnds (lev, d2) float32 480B dask.array<chunksize=(60, 2), meta=np.ndarray>
so (time, lev, nlat, nlon) float32 58GB dask.array<chunksize=(4, 60, 384, 320), meta=np.ndarray>
nlon_bnds (nlon, bnds) float64 5kB 0.5 1.5 1.5 2.5 ... 319.5 319.5 320.5
thetao (time, lev, nlat, nlon) float32 58GB dask.array<chunksize=(4, 60, 384, 320), meta=np.ndarray>
Attributes: (12/46)
Conventions: CF-1.7 CMIP-6.2
activity_id: CMIP
case_id: 15
cesm_casename: b.e21.BHIST.f09_g17.CMIP6-historical.001
contact: cesm_cmip6@ucar.edu
creation_date: 2019-01-16T23:15:40Z
... ...
sub_experiment_id: none
branch_time_in_parent: 219000.0
branch_time_in_child: 674885.0
branch_method: standard
further_info_url: https://furtherinfo.es-doc.org/CMIP6.NCA...
DODS_EXTRA.Unlimited_Dimension: time2. Create the output grid#
Related API: xcdat.create_grid()
In this example, we will generate a vertical grid with a linear spaced level coordinate using xcdat.create_grid
Alternatively a grid can be loaded from a file, e.g.
grid_urlpath = "http://aims3.llnl.gov/thredds/dodsC/css03_data/CMIP6/CMIP/NOAA-GFDL/GFDL-CM4/abrupt-4xCO2/r1i1p1f1/day/tas/gr2/v20180701/tas_day_GFDL-CM4_abrupt-4xCO2_r1i1p1f1_gr2_00010101-00201231.nc"
grid_ds = xcdat.open_dataset(grid_urlpath)
output_grid = grid_ds.regridder.grid
[3]:
output_grid = xcdat.create_grid(
z=xcdat.create_axis("lev", np.linspace(5, 537, 10))
)
output_grid
[3]:
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 240B
Dimensions: (lev: 10, bnds: 2)
Coordinates:
* lev (lev) float64 80B 5.0 64.11 123.2 182.3 ... 418.8 477.9 537.0
Dimensions without coordinates: bnds
Data variables:
lev_bnds (lev, bnds) float64 160B -24.56 34.56 34.56 ... 507.4 507.4 566.63. Regridding using the linear method#
Related API: xarray.Dataset.regridder.vertical()
Here we will regrid the input data to the output grid using the xgcm tool and the linear method.
We’ll interpolate salinity onto the new vertical grid.
[4]:
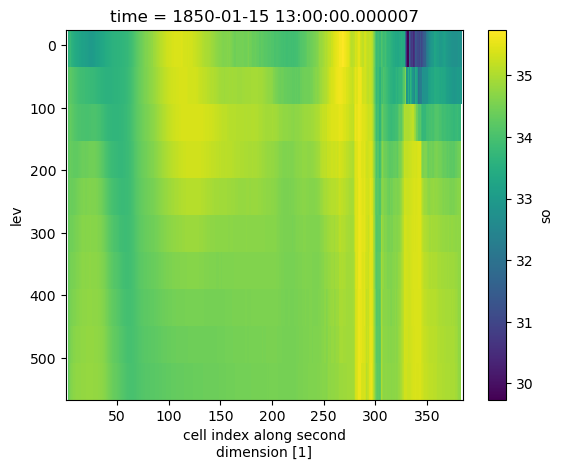
output = ds.regridder.vertical("so", output_grid, tool="xgcm", method="linear")
output.so.isel(time=0).mean(dim="nlon").plot()
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
2024-04-17 16:52:34,563 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:34,563 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
4. Regridding from depth to density space#
Related API: xarray.Dataset.regridder.vertical()
Here we will regrid the input data to the output grid using the xgcm tool and the linear method.
We’ll remap salinity into density space.
[5]:
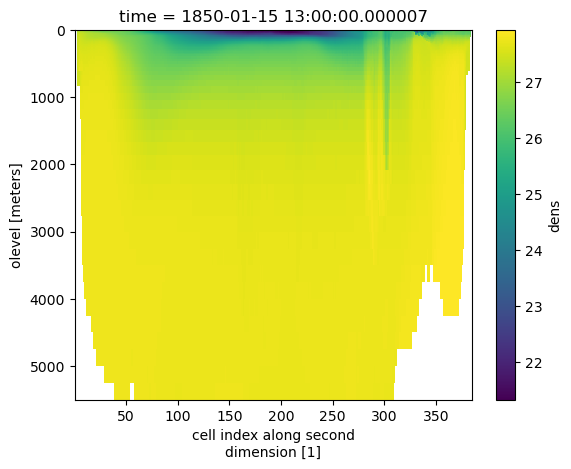
# Apply gsw function to calculate potential density from potential temperature (thetao) and salinity (so)
ds["dens"] = gsw.sigma0(ds.so, ds.thetao)
ds.dens.isel(time=0).mean(dim="nlon").plot()
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
[6]:
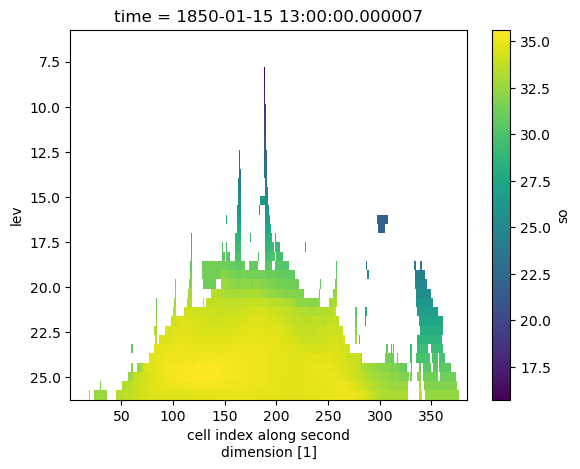
density_grid = xcdat.create_grid(
z=xcdat.create_axis("lev", np.linspace(6, 26, 40))
)
output = ds.regridder.vertical("so", density_grid, tool="xgcm", method="linear", target_data="dens")
output.so.isel(time=0).mean(dim="nlon").plot()
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
2024-04-17 16:52:43,882 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:43,882 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
5. Regridding using the conservative method#
Related API: xarray.Dataset.regridder.vertical()
Here we will regrid the input data to the output grid using the xgcm tool and the conservative method.
We’ll transform model levels using conservative regridding. In order to perform the regridding we’ll need two grid positions, the lev coordinate is center and we”ll create the outer points using cf_xarray”s bounds_to_vertices.
[7]:
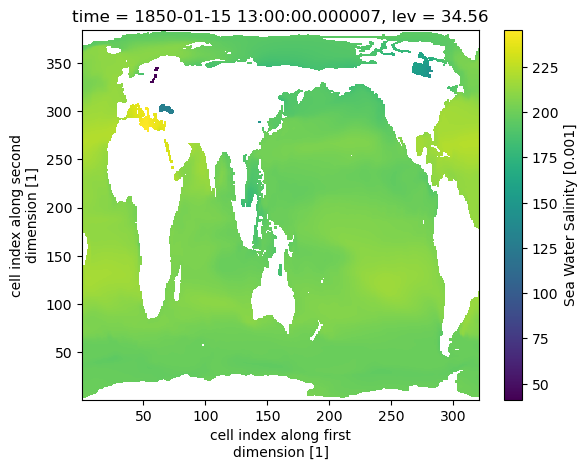
ds_olev = ds.cf.bounds_to_vertices("lev").rename({"lev_vertices": "olev"})
output = ds_olev.regridder.vertical("so", output_grid, tool="xgcm", method="conservative", grid_positions={"center": "lev", "outer": "olev"})
output.so.isel(time=0).sel(lev=0, method="nearest").plot()
2024-04-17 16:52:50,627 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
2024-04-17 16:52:50,627 [WARNING]: bounds.py(add_missing_bounds:191) >> The nlat coord variable has a 'units' attribute that is not in degrees.
[7]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x19793db80>
Example 2: Remapping Atmosphere Variables#
1. Open dataset#
[8]:
# Url of data from the E3SM model in CMIP6
url_ta = 'https://esgf-data2.llnl.gov/thredds/dodsC/user_pub_work/CMIP6/CMIP/E3SM-Project/E3SM-2-0/historical/r1i1p1f1/Amon/ta/gr/v20220830/ta_Amon_E3SM-2-0_historical_r1i1p1f1_gr_185001-189912.nc'
url_cl = 'https://esgf-data2.llnl.gov/thredds/dodsC/user_pub_work/CMIP6/CMIP/E3SM-Project/E3SM-2-0/historical/r1i1p1f1/Amon/cl/gr/v20220830/cl_Amon_E3SM-2-0_historical_r1i1p1f1_gr_185001-189912.nc'
ds_ta = xcdat.open_dataset(url_ta, chunks={"time": 4}, add_bounds=["Z"])
ds_cl = xcdat.open_dataset(url_cl, chunks={"time": 4})
2. Create the output grid#
Related API: xcdat.create_grid()
In this example, we will generate a grid with a linear spaced level coordinate.
[9]:
output_grid = xcdat.create_grid(
z=xcdat.create_axis("lev", np.linspace(100000, 1, 13))
)
output_grid
[9]:
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 312B
Dimensions: (lev: 13, bnds: 2)
Coordinates:
* lev (lev) float64 104B 1e+05 9.167e+04 8.333e+04 ... 8.334e+03 1.0
Dimensions without coordinates: bnds
Data variables:
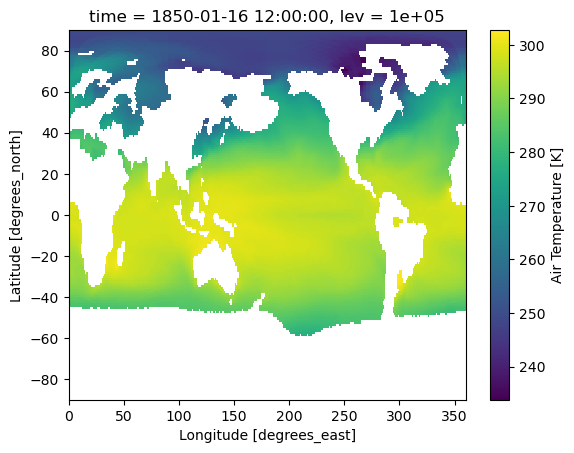
lev_bnds (lev, bnds) float64 208B 1.042e+05 9.583e+04 ... -4.166e+033. Remapping air temperature on pressure levels to a set of target pressure levels.#
Related API: xarray.Dataset.regridder.vertical()
Here we will regrid the input data to the output grid using the xgcm tool and the log method.
We’ll remap pressure levels.
[10]:
# Remap from original pressure level to target pressure level using logarithmic interpolation
# Note: output grids can be either ascending or descending
output_ta = ds_ta.regridder.vertical("ta", output_grid, method="log")
output_ta.ta.isel(time=0, lev=0).plot()
[10]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x197a6f560>
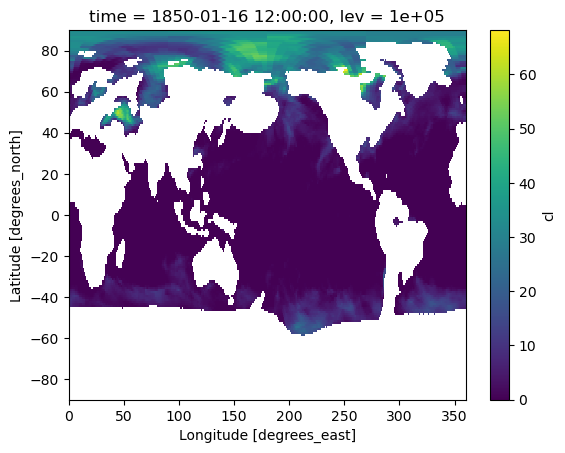
4: Remap cloud fraction from model hybrid coordinate to pressure levels#
Related API: xarray.Dataset.regridder.vertical()
Here we will regrid the input data to the output grid using the xgcm tool and the linear method.
We’ll remap cloud fraction into pressure space.
[11]:
# Build hybrid pressure coordinate
def hybrid_coordinate(p0, a, b, ps, **kwargs):
return a*p0 + b*ps
pressure = hybrid_coordinate(**ds_cl.data_vars)
pressure
[11]:
<xarray.DataArray (lev: 72, time: 600, lat: 180, lon: 360)> Size: 22GB dask.array<add, shape=(72, 600, 180, 360), dtype=float64, chunksize=(72, 4, 180, 360), chunktype=numpy.ndarray> Coordinates: * lev (lev) float64 576B 0.9985 0.9938 0.9862 ... 0.0001828 0.0001238 * lat (lat) float64 1kB -89.5 -88.5 -87.5 -86.5 ... 86.5 87.5 88.5 89.5 * lon (lon) float64 3kB 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 ... 356.5 357.5 358.5 359.5 * time (time) object 5kB 1850-01-16 12:00:00 ... 1899-12-16 12:00:00
[12]:
new_pressure_grid = xcdat.create_grid(
z=xcdat.create_axis("lev", np.linspace(100000, 1, 13))
)
output_cl = ds_cl.regridder.vertical("cl", new_pressure_grid, method="linear", target_data=pressure)
output_cl.cl.isel(time=0, lev=0).plot()
[12]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x1979ef6e0>
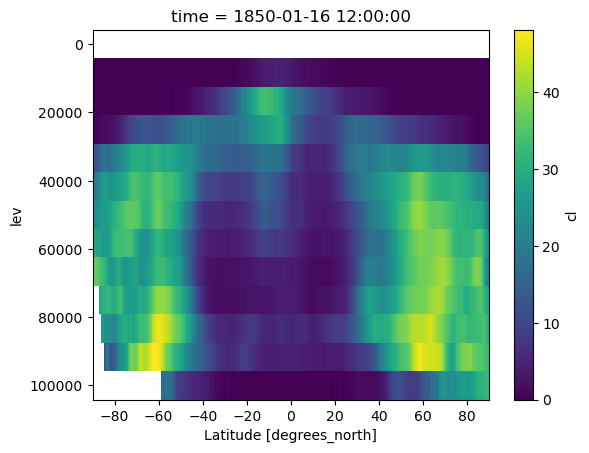
[13]:
output_cl.cl.isel(time=0).mean(dim='lon').plot()
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
[ ]:
